Câu hỏi và đáp án bài Reading Test 2 passage 2 - IELTS Cambridge 5 - What's so funny?
tip
Xem đáp án bên dưới.
Questions 14-20
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 2?
In boxes 14-20 on your answer sheet, write
- TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
- FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
- NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
- Arthur Koestler considered laughter biologically important in several ways.
- Plato believed humour to be a sign of above-average intelligence.
- Kant believed that a successful joke involves the controlled release of nervous energy.
- Current thinking on humour has largely ignored Aristotle's view on the subject.
- Graeme Ritchie's work links jokes to artificial intelligence.
- Most comedians use personal situations as a source of humour.
- Chimpanzees make particular noises when they are playing.
Questions 21-23
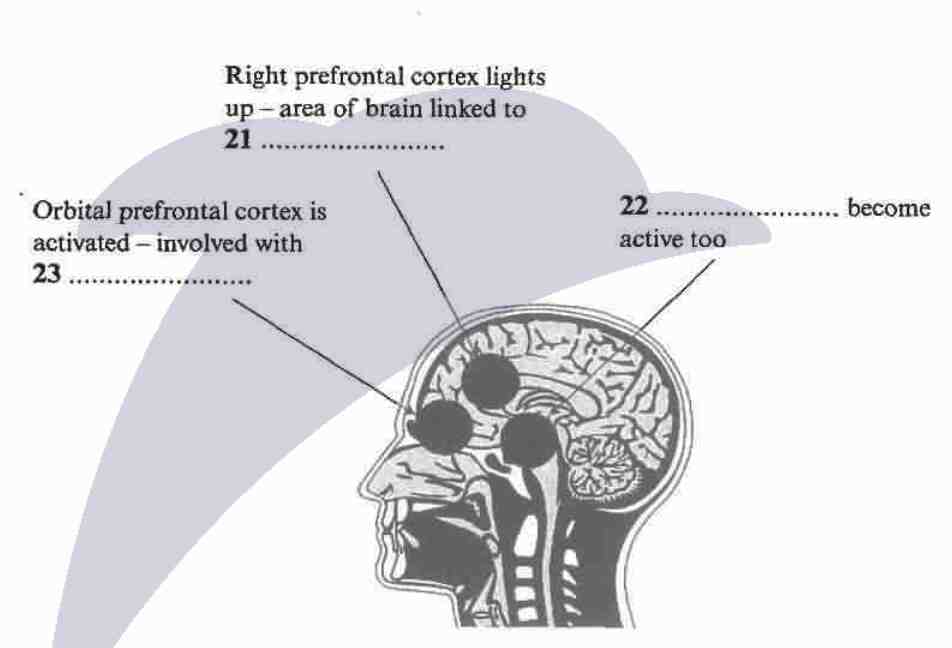
The diagram below shows the areas of the brain activated by jokes.
Label the diagram.
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 21-23 on your answer sheet.
-
Right prefrontal cortex lights up - area of brain linked to 21 ......................
-
22 ...................... become active too
-
Orbital prefrontal cortex is activated - involved with 23 ......................
Questions 24-27
Complete each sentence with the correct ending A-G below.
Write the correct letter A-G in boxes 24-27 on your answer sheet.
- One of the brain's most difficult tasks is to
- Because of the language they have developed, humans
- Individual responses to humour
- Peter Derks believes that humour
- A react to their own thoughts.
- B helped create language in humans.
- C respond instantly to whatever is happening.
- D may provide valuable information about the operation of the brain.
- E cope with difficult situations.
- F relate to a person's subjective views.
- G led our ancestors to smile and then laugh.
Đáp án
Bấm để xem đáp án
Reading Passage 2, Questions 14-27
- FALSE
- NOT GIVEN
- TRUE
- FALSE
- TRUE
- NOT GIVEN
- TRUE
- problem solving
- temporal lobes
- evaluating information
- C
- A
- F
- D